Table of Contents
- Why Cybersecurity Matters for Small Businesses
- How Cybersecurity Helps in Small Businesses
- Types of Cybersecurity Threats for Small Businesses
- 7 Cost-Effective Cybersecurity Solutions for SMBs
- 1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) / 2FA
- 2. Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
- 3. Firewall / Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
- 4. Virtual Private Network (VPN) or Zero-Trust Remote Access
- 5. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) / Log Aggregation & Alerting
- 6. Employee Training & Phishing Simulations
- 7. Backup, Patch Management & Incident Response Planning
- Cost-effective Cybersecurity Tools and Strategies
- How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Company for My SMB?
- How to Implement a Cybersecurity Strategy for Small Businesses
- FAQ – Cybersecurity Solutions
- 1. How to protect your small business from cyber attacks?
- 2. What are the most effective cybersecurity strategies for small businesses to protect against data breaches and ransomware attacks in 2025?
- 3. How to implement a cybersecurity strategy for small businesses?
- 4. How can small businesses implement enterprise-level cybersecurity on a budget?
- 5. What are the key solutions for cybersecurity in SMBs?
- Conclusion
Cost-effective cybersecurity solutions start with smart prioritization, not costly overhauls. As small firms manage tight budgets, you don’t have to overspend to stay protected. Explore our full cybersecurity guide for budget-conscious SMBs to learn how to strengthen your defenses affordably.
Cybersecurity for small businesses is often misunderstood; many think it’s an all-or-nothing deal. However, with the right combination of strategy, tools, and discipline, you can gradually build strong defenses.
Why Cybersecurity Matters for Small Businesses
Even though many small businesses believe they’re “too small to be targeted,” the data tells a different story:
- Approximately 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses.
- The average cost of a cyberattack on an SMB is around $254,445, with high-end cases reaching $7 million.
- Up to 60% of small firms shut down within six months after a breach.
- Many small businesses are underprepared: only 14% rate their cybersecurity capability as “highly effective.”
- Two-thirds of SMBs say cost prevents them from upgrading security tools.
- 58% of SMBs spent more than planned on cybersecurity in 2024, and 57% now rank it among their top priorities.
These statistics highlight a simple but powerful truth: inadequate security costs more in the long run. Viewing cybersecurity spending as just an “expense” often overlooks the bigger risk of a breach. Instead, it should be seen as insurance against disruption, reputational harm, regulatory fines, lost customers, and even potential existential threats.
How Cybersecurity Helps in Small Businesses
Before we dive into tools, let’s clarify the roles that cybersecurity plays in an SME (small-to-medium enterprise):
- Resilience
Even if a threat slips in, good security limits the damage, shortens recovery time, and ensures business continuity. - Trust & Reputation
Customers, partners, and vendors increasingly expect proof of cyber hygiene. A breach can erode trust irreparably. - Compliance & Liability Mitigation
Whether GDPR, CCPA, PCI-DSS, or local data laws, proper controls help avoid fines and legal exposure. - Operational Stability
Preventing downtime, data loss, or ransomware means you keep your operations humming. - Strategic Differentiator
In certain markets (e.g., in healthcare, fintech, and B2B SaaS), strong security can become a selling point.
Let me use a metaphor: imagine your business as a house. A strong door, a security camera, and a locked gate don’t stop 100% of burglars—but they deter most, slow down others, and allow easier recovery if a break-in happens. Cybersecurity is your digital “locks, cameras, alarms, and insurance.”
Types of Cybersecurity Threats for Small Businesses
Understanding what you’re protecting against helps you pick the right defenses. Here are frequent threats for SMBs:
| Threat | Why It’s Dangerous | Example |
| Phishing / Spear-phishing | Employees are tricked into clicking on malicious links or giving their credentials | A staff member receives a fake invoice email and enters credentials |
| Ransomware | Attackers encrypt your files, demand payment | An entire server farm is locked until ransom is paid |
| Malware / Trojans / Infostealers | Malicious code quietly exfiltrates or corrupts data | Spyware sending customer lists to cybercriminals |
| Insider threats | Disgruntled or negligent staff leak, misuse, or misconfigure systems | A former employee still has access and deletes backups |
| Data breaches | Unauthorized access to sensitive records | Customer PII, payment data, or proprietary docs get exposed |
| Zero-day attacks / advanced exploits | New vulnerabilities are being exploited before patches are available | A flaw in a widely used library was exploited before anyone knew |
| Password attacks & credential reuse | Weak passwords or reused credentials across systems | Using the same password for email and the internal admin portal |
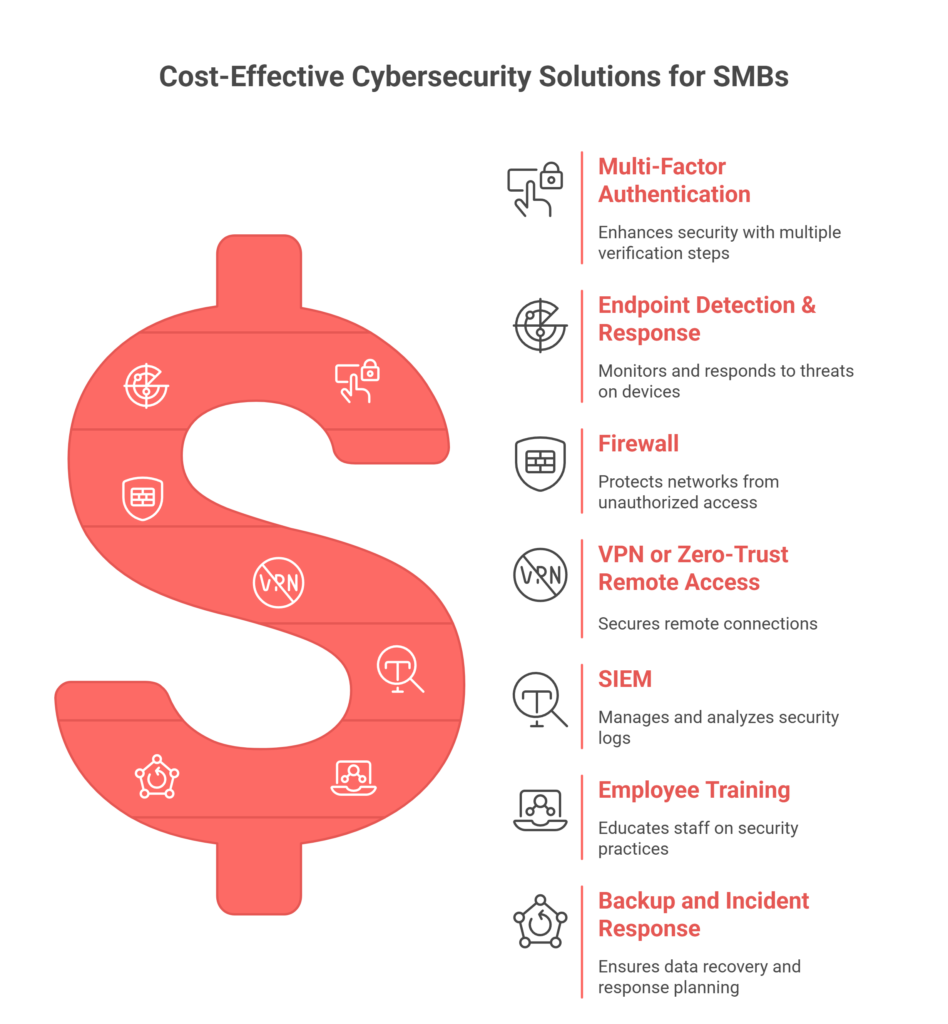
7 Cost-Effective Cybersecurity Solutions for SMBs
Many SMBs rely on external partners offering MDR services to provide continuous threat detection and rapid incident response without expanding internal headcount. Below are seven core solutions that can move you from “exposed” to “reasonably secure,” even on a budget.
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) / 2FA
This is low-hanging fruit. Require MFA for email, VPN, admin portals, cloud services, and remote access.
Benefits: Drastically reduces credential-based breaches, often without significant cost (many cloud platforms include it for free or low cost).
2. Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
Go beyond traditional antivirus. EDR solutions detect malicious behavior, isolate endpoints, and help recover.
- Many modern EDR offerings are value-priced for SMB use cases.
3. Firewall / Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
A properly configured firewall (ideally with application-aware rules) is foundational to network security.
- Use one if you don’t already, or upgrade the firmware to the latest, segment internal traffic, and enable logging.
4. Virtual Private Network (VPN) or Zero-Trust Remote Access
For remote workers or branch offices, encrypt traffic via VPN or use zero-trust access tools that validate each connection.
5. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) / Log Aggregation & Alerting
You don’t need a massive SIEM out of the box. Start with a lightweight log management tool or open-source option, aggregate logs centrally, and set alerts for unusual events.
6. Employee Training & Phishing Simulations
Humans are often the weakest link. Regular training, simulated phishing tests, and policies (e.g., least privilege, access review) are among the highest ROI measures.
7. Backup, Patch Management & Incident Response Planning
- Backup: Regular, tested, off-site backups (or immutable backups) are non-negotiable.
- Patch management: Apply security updates promptly.
- Incident response: Even a basic playbook helps limit damage when things go wrong.
Cost-effective Cybersecurity Tools and Strategies
Tools like SiteLock and Heimdal help safeguard your sites and applications. For deeper analysis, consider regular VAPT Testing to identify vulnerabilities before attackers do.
Top Cost-Effective Tools
| Tool / Service | Main Protection Features | Typical Pricing | Notes |
| Bitdefender GravityZone | Antivirus, EDR, threat protection, and central management | Competitive, tiered plans | Fast detection, multi-year discounts |
| CrowdStrike Falcon Go | AI antivirus, endpoint & mobile protection, managed support | $59.99/device/year | Scalable, suitable for small teams |
| Cynet All-in-One | Endpoint, network, user threat detection & response (XDR) | From ~$7/endpoint/month | Automated, ideal for <10 devices |
| Snort (Open Source) | Intrusion prevention, network IDS/IPS | Free | Needs configuration/maintenance |
| SolarWinds Security Event | Log collection, automated threat detection, dashboards | Budget-friendly | Good for small fleets |
| Heimdal Security | Unified protection (cloud, email, DNS, ransomware) | Affordable modular pricing | Choose modules based on your risk profile |
| SiteLock | Website protection, malware scanning, vulnerability scans | Paid, with 30-day trial | Especially useful for e-commerce / CMS sites |
“ CrowdStrike Falcon Go provides SMBs with $59.99 worth of cybersecurity per device annually, removing cost and saving time for small businesses.” (This line adapted for narrative emphasis; actual published marketing claims may vary.)
Strategy Tips for Maximizing ROI
- Start with defense in depth: Even cheap layers (MFA + EDR + backups) dramatically reduce risk compared to no layers.
- Use open-source wisely: Tools like Snort or OSSIM are powerful — but require capable staff or contractor support.
- Bundle where possible: Many vendors offer combined suites (e.g., endpoint + email + DNS) at a discount.
- Manage licensing yearly: Opt for multi-year contracts only if discounts are significant and commitment is safe.
- Audit what you already own: Many businesses already have built-in tools (e.g., Microsoft Defender, firewall logs) that are underused.
How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Company for My SMB?
Before partnering with a vendor, it’s important to assess compatibility, pricing transparency, and scalability. For a deeper breakdown, check our guide on choosing the right cybersecurity solution for your business. Below is guidance and a comparison:
Key Evaluation Criteria
- SMB Focus & Understanding
A vendor experienced with small-to-medium businesses will better navigate your constraints and priorities.
- Transparent Pricing & Bundling Flexibility
Beware providers that lock you into expensive modules you don’t need.
- Support & Managed Services Depth
Ensure they offer meaningful monitoring, threat hunting, and incident response, not just tools.
- Scalability & Modularity
As you grow, you should be able to add new modules or increase coverage.
- Compliance Expertise
If you must comply with regulations (GDPR, PCI, ISO 27001), choose a partner who can help with assessments and audits.
- Integration & Compatibility
Their tools must work with your existing systems (cloud, on-prem, hybrid).
- References & Track Record
Ask for case studies, especially within your industry.
How to Implement a Cybersecurity Strategy for Small Businesses
Here’s a step-by-step roadmap you (as Head of IT or CTO) can follow to roll out improvements steadily without intimidating the CEO or overcommitting resources.
Step-by-Step Roadmap in Cybersecurity Strategy
| Phase | Key Activities | Outcome |
| Assessment & Baseline | Risk assessment, gap analysis, asset inventory, stakeholder interviews | You know your current posture and biggest vulnerabilities |
| Quick Wins & Foundation | Deploy MFA, patch critical systems, secure backups, firewall hardening, and standard user rights | You raise the floor of security rapidly |
| Tool Deployment & Monitoring | Roll out EDR, centralized log collection, alerting rules, initial SIEM, or a lightweight alternative | Real-time detection and visibility |
| Training & Culture | Begin employee training, phishing simulations, and role-based access reviews | User awareness and reduced human risk vector |
| Incident Playbooks & Insurance | Develop an incident response plan, test it, and consider cyber liability insurance | You’re ready to act when something happens |
| Growth & Optimization | Add modules (cloud, email, DNS security), continual tuning, and regular audits. | You refine defenses as you scale |
FAQ – Cybersecurity Solutions
1. How to protect your small business from cyber attacks?
Start with the basics: require MFA, keep software and operating systems patched, perform regular backups, restrict user access, and educate staff with phishing simulations. Use a lightweight but capable endpoint security solution, gradually layer log monitoring, and develop a response plan.
2. What are the most effective cybersecurity strategies for small businesses to protect against data breaches and ransomware attacks in 2025?
The most effective strategies combine defense in depth (MFA, EDR, segmentation), user training to reduce phishing risk, rapid patching, secure backups (with air-gap or immutable copies), and continuous monitoring. Also consider teaming with an MSSP or MDR service for 24/7 oversight.
3. How to implement a cybersecurity strategy for small businesses?
Begin with a risk assessment, identify key assets, prioritize threats, then phase your deployment: quick wins (MFA, patching), deploy detection tools, train employees, and build incident response playbooks. Review and iterate quarterly to adapt to evolving threats.
4. How can small businesses implement enterprise-level cybersecurity on a budget?
By selecting modular, affordable tools tailored to core needs (EDR, MFA, backups), using open-source or built-in tools (e.g., Microsoft Defender), partnering with an MSSP/MDR, automating alerts, and shifting risk posture incrementally rather than all at once.
5. What are the key solutions for cybersecurity in SMBs?
Key solutions include: MFA/2FA, EDR, firewall / NGFW, secure VPN or remote access, log monitoring/ SIEM, regular employee training, disciplined patching & backups, and choosing a trusted cybersecurity solutions provider or MSSP.
Conclusion
Small businesses don’t need massive budgets to stay secure. With layered, cost-effective cybersecurity solutions, strong policies, and the right partners, you can protect data, maintain trust, and keep operations running smoothly.
Start with quick wins—MFA, backups, employee training—and build upward. Every small improvement compounds your defense. Partner with a trusted cybersecurity solutions provider to scale your protection confidently and cost-effectively.
Technical Consultant
Passionate about driving digital transformation through innovative IT solutions. Experienced in bridging business needs with technical strategies, ensuring seamless implementation, optimizing systems, and staying ahead with emerging technologies to deliver measurable impact and long-term value for clients across industries.




